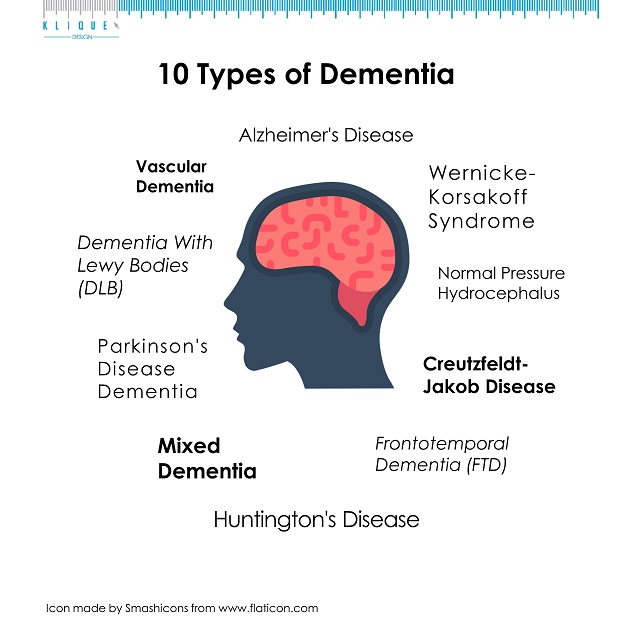
Dementia is a form of cognitive disability. It refers to the loss of thinking and memory abilities that are significant enough to impact one’s everyday life. It is not a normal process of aging but the results of several brain diseases.
Dementia is not a disease but a syndrome. Symptoms, treatments and care are different for different types of dementia.
Alzheimer’s Disease
This is a common type of dementia. The symptoms are mild at the beginning but get worse over time. People with Alzheimer will have difficulties in planning, carrying familiar tasks and memory loss.
Vascular Dementia
Stroke can cause vascular dementia. It is common for a vascular dementia patient to suffer from Alzheimer’s disease at the same time.
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)
DLB is caused by microscopic deposits of a protein in patient’s cortex. Besides memory loss, patient experiences difficulties in paying attention, visual hallucinations, unusual sleepiness and movement.
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia
About 50% to 80% Parkinson’s disease patients get this type of dementia. Generally, dementia symptoms develop 10 years after a person get Parkinson’s. Patients have the same symptoms as Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB).
Mixed Dementia
This refers to a combination of 2 types of dementia.
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
Frontal lobe which controls our reasoning, emotions, judgment, and voluntary movement. Cell damage in this area of our brain will lead to FTD.
Huntington’s Disease
It is a progressive brain disorder caused by inherited genetic defect that results in death of brain cells. Symptoms usually appear in a person’s 30s or 40s.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
CJD is a rare and fatal degenerative brain disorder. Prion, a type of protein is causing normally folded protein in the brain to misfold. It happens suddenly and get worsen quickly. Generally, 70% of people die within a year of diagnosis.
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)
This form of neurological disorder also known as Hakim’s syndrome and symptomatic hydrocephalus. The blocking of the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through the brain and spinal cords is causing the build-up of CSF in the brain and leads to NPH.
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS)
Chronic heavy drinking and severe deficiency of vitamin B-1, or Thiamine in the body can lead to WKS. Usually it does not affect one’s problem-solving and thinking skills.